Evaluation Points and Criteria
In this “Evaluation” part, the performances of the 36 countries surveyed in this project are evaluated numerically in three areas—that is, nuclear disarmament, non-proliferation and nuclear security—based upon study and analysis compiled in the “Report” section.
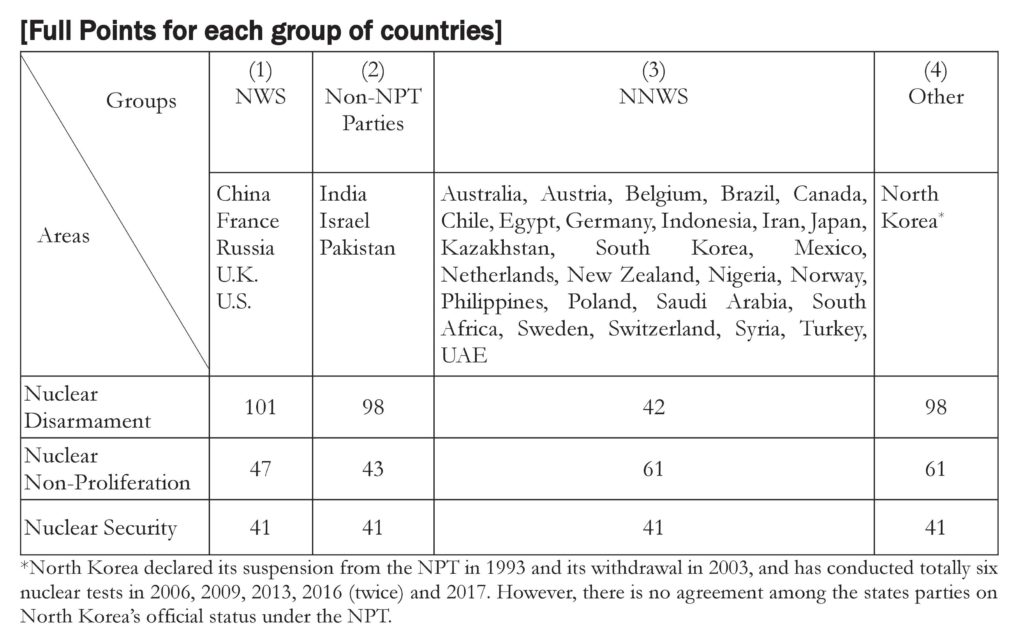
Evaluations of the four groups—nuclear-weapon states (NWS), non-parties to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), non-nuclear-weapon states (NNWS), and one particular state (North Korea)—are made separately because of their different characteristics. Since different sets of criteria are applied to different groups of countries, full points differ according to the group each country belongs to. Then, as a measure to visualize a comparison of 36 countries’ relative performances, each country’s performance in each area is shown on a chart in percentage terms.
The Following lists the point values and scale of measurement of each evaluation criteria.
【Nuclear Disarmament】
| Evaluation criteria | Maximum points |
Scale of measurement |
| 1. Status of Nuclear Forces (estimates) | -20 | |
| Status of nuclear forces (estimates) | (-20) | -5 (〜50); -6 (51〜100); -8 (101〜200); -10 (201〜400); -12 (401〜1,000); -14 (1,001〜2,000); -16 (2,001〜 4,000); -17 (4,001〜6,000); -19 (6,001〜8,000); -20 (8,001〜) |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| 2. Commitment to Achieving a World without Nuclear Weapons | 11 | |
| A) Voting behavior on UNGA resolutions on nuclear disarmament proposals by Japan, NAC and NAM | (6) | On each resolution: 0 (against); 1 (abstention); 2 (in favor) |
| B) Announcement of significant policies and important activities | (3) | Add 1 point for each policy, proposal and other initiatives having a major impact on global momentum toward a world without nuclear weapons (maximum 3 points) |
| -3~-1 (activities that are not covered by the existing evaluation items but contrary to nuclear disarmament) | ||
| C) Humanitarian consequences of nuclear weapons | (2) | On each resolution: 0 (against); 0.5(abstention); 1 (in favor) |
| 3. Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW) | 10 | |
| A) Signing and ratifying the TPNW | (7) | 0 (not signing); 3 (not ratifying); 7 (ratifying) |
| B) Voting behavior on UNGA resolutions on a legal prohibition of nuclear weapons | (3) | On each resolution: 0 (against); 0.5 (abstention); 1 (in favor) |
| 4. Reduction of Nuclear Weapons | 22 | |
| A) Reduction of nuclear weapons | (15) | ・Add 1~10 points in accordance with the decuple rate of reduction from the previous fiscal year for a country having declared the number of nuclear weapons ・For a country having not declared it, add some points using the following formula: (the previous target – the latest target)÷the estimated number of nuclear weapons×10 ・Add 1 (engaging in nuclear weapons reduction over the past 5 years); add 1 (engaging in nuclear weapons reduction under legally-binding frameworks such as New Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty); add 1 (announcing further reduction plan and implementing it in 2021) ・Give a full score (15 points) in case of the total abolition of nuclear weapons ・-1 (increase of the number of possessed nuclear weapons in the past five years without any reductions) |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| B) Concrete plans for further reduction of nuclear weapons |
(3) | 0 (no announcement on a plan of nuclear weapons reduction); 1 (declaring a rough plan of nuclear weapons reduction); 2 (declaring a plan on the size of nuclear weapons reduction); 3 (declaring a concrete and detailed plan of reduction) |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| C) Trends on strengthening/modernizing nuclear weapons capabilities | (4) | 0 (modernizing/reinforcing nuclear forces in a backward move toward nuclear weapons reduction); 2~3 (modernizing/reinforcing nuclear forces which may not lead to increasing the number of nuclear weapons); 4 (not engaging in nuclear modernization/reinforcement) |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| 5. Diminishing the Roles and Significance of Nuclear Weapons in National Security Strategies and Policies | 8 | |
| A) Current status of the roles and significance of nuclear weapons | (-8) | -8~-7 (judged based on the declaratory policy) |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| B) Commitment to no first use, “sole purpose,” and related doctrines | (3) | 0 (not adopting either policy); 2 (adopting a similar policy or expressing its will to adopt either policy in the future); 3 (already adopting either policy) |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| C) Negative security assurances | (2) | 0 (not declaring); 1 (declaring with reservations); 2 (declaring without reservations) |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| D) Signing and ratifying the protocols of the treaties on nuclear-weapon-free zones | (3) | Add 0.5 point for the ratification of one protocol; a country ratifying all protocols marks 3 points |
| (not applicable to countries except NWS) | ||
| E) Relying on extended nuclear deterrence | (-5) | (not applicable to the NWS and Non-NPT Parties) |
| (applied solely to the NNWS): -5 (a country relying on the nuclear umbrella and participating in nuclear sharing); -3 (a country relying on the nuclear umbrella); 0 (a country not relying on the nuclear umbrella) | ||
| 6. De-alerting or Measures for Maximizing Decision Time to Authorize the Use of Nuclear Weapons | 4 | |
| De-alerting or measures for maximizing decision time to authorize the use of nuclear weapons | (4) | 0~1 (maintaining a high alert level); 2 (maintaining a certain alert level); 3 (de-alerting during peacetime); add 1 point for implementing measures for increasing the credibility of (lowered) alert status (not applicable to the NNWS) |
| 7. CTBT | 11 | |
| A) Signing and ratifying the CTBT | (4) | 0 (not signing); 2 (not ratifying); 4 (ratifying) |
| B) Moratoria on nuclear test explosions pending CTBT’s entry into force | (3) | 0 (not declaring); 2 (declaring); 3 (declaring and closing nuclear test sites) |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| C) Cooperation with the CTBTO Preparatory Commission | (2) | 0 (no cooperation or no information); 1~2 (paying contributions, actively participating in meetings, and actively engaging in outreach activities for the treaty’s entry into force) |
| D) Contribution to the development of the CTBT verification systems | (2) | Add 1 point for establishing and operating the IMS; add another 1 point for participating in the discussions on enhancing the CTBT verification capabilities |
| E) Nuclear testing | (-3) | -3 (conducting nuclear test explosions in the past 5 years);-1 (conducting nuclear tests without explosions or tests with unclear status); 0 (not conducting any nuclear tests) |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| 8. FMCT | 10 | |
| A) Commitment, efforts, and proposals toward immediate commencement of negotiations on an FMCT | (5) | Add 1 (expressing a commitment); add 1~2 (actively engaging in the promotion of early commencement); add 1~2 (making concrete proposals on the start of negotiations) |
| B) Moratoria on the production of fissile material for use in nuclear weapons | (3) | 0 (not declaring); 1 (not declaring but not producing fissile material for nuclear weapons); 2 (declaring); 3 (declaring and taking measures for the cessation of production as declared) |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| C) Contribution to the development of verification measures | (2) | 0 (no contribution or no information); 1 (proposing research on verification measures); 2 (engaging in R&D for verification measures) |
| 9. Transparency in Nuclear Forces, Fissile Material for Nuclear Weapons, and Nuclear Strategy/Doctrine | 6 | |
| Transparency in nuclear forces, fissile material for nuclear weapons, and nuclear strategy/doctrine | (6) | Add 1~2 (disclosing the nuclear strategy/doctrine); add 1~2 (disclosing the status of nuclear forces); add 1~2 (disclosing the status of fissile material usable for nuclear weapons) |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| 10. Nuclear Disarmament Verifications | 7 | |
| A) Acceptance and implementation of nuclear disarmament verification | (3) | 0 (not accepting or implementing); 2 (limited acceptance and implementation); 3 (accepting and implementing verification with comprehensiveness and completeness); deduct 1~2 points in case of non-compliance or problems in implementation |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| B) Engagement in research and development for verification measures of nuclear disarmament | (1) | 0 (not engaging or no information); 1 (engaging in R&D) |
| C) The IAEA inspections to fissile material declared as no longer required for military purposes | (3) | 0 (not implementing); 1(limited implementation); 3 (implementing); add 1 point if a country engages in efforts for implementing or strengthening implementation, except in the case of already implementing |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| 11. Irreversibility | 7 | |
| A) Implementing or planning dismantlement of nuclear warheads and their delivery vehicles | (3) | 0 (not implementing or no information); 1 (perhaps implementing but not clear); 2~3 (implementing) |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| B) Decommissioning/conversion of nuclear weapons-related facilities | (2) | 0 (not implementing or no information); 1 (implementing in a limited way); 2 (implementing extensively) |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| C) Measures for fissile material declared excess for military purposes, such as disposition or conversion to peaceful purposes | (2) | 0 (not implementing or no information); 1 (implementing in a limited way); 2 (implementing extensively) |
| (not applicable to the NNWS) | ||
| 12. Disarmament and Non-Proliferation Education and Cooperation with Civil Society | 4 | |
| Disarmament and non-proliferation education and cooperation with civil society | (4) | Add 1 (mentioning in a statement or participating in the joint statement or mentioning at the NPT PrepCom/RevCon, etc); add 1~2 (implementing disarmament and non-proliferation education); add 1~2 (cooperating with civil society); maximum 4 points |
| 13. Hiroshima and Nagasaki Peace Memorial Ceremonies | 1 | |
| Hiroshima and Nagasaki Peace Memorial Ceremonies | (1) | 0 (not attending);0.5 (not attending in 2021 but has attended at least once during the past 3 years); 1 (attending any one of the ceremonies) |
【Nuclear Non-Proliferation】
| Evaluation criteria | Maximum points |
Scale of measurement |
| 1. Acceptance and Compliance with Nuclear Non-Proliferation Obligations | 20 | |
| A) Accession to the NPT | (3) | 0 (not signing or declaring withdrawal); 3 (not ratifying); 10 (in force) |
| B) Compliance with Articles I and II of the NPT and the UNSCRs on non-proliferation | (7) | 0 (not complying with Articles I and II of the NPT); 3~4 (having not yet violated Articles I and II of the NPT but displaying behaviors that raise concerns about proliferation, or not complying with the UNSCRs adopted for relevant nuclear issues); 5 (taking concrete measures for solving the non-compliance issue); 7 (complying) |
| As for the non-NPT states (maximum 3 points); 2 (not complying with the UNSCRs adopted for relevant nuclear issues); 3 (other cases) | ||
| -4~-1 (activities that are not covered by the existing evaluation items but contrary to nuclear non-proliferation) | ||
| C) Nuclear-Weapon-Free Zones | (3) | 1 (signing the NWFZ treaty); 3 (ratifying the treaty) |
| 2. IAEA Safeguards Applied to the NPT NNWS | 18 | |
| A) Signing and ratifying a Comprehensive Safeguards Agreement | (4) | 0 (not signing); 1 (not ratifying); 4 (in force) |
| B) Signing and ratifying an Additional Protocol | (5) | 0 (not signing); 1 (not ratifying); 3 (provisional application); 5 (in force) |
| C) Implementation of the integrated safeguards | (4) | 0 (not implementing); 2 (broader conclusion) 4 (implementing) |
| D) Compliance with IAEA Safeguards Agreement | (5) | 0 (not resolving the non-compliance issue); 2 (taking concrete measures for solving the non-compliance issue); 5 (complying) |
| 3. IAEA Safeguards Applied to NWS and Non-Parties to the NPT | 7 | |
| A) Application of the IAEA safeguards (Voluntary Offer Agreement or INFCIRC/66) to their peaceful nuclear in facilities | (3) | 0 (not applying); 2 (applying INFCIRC/66); 3 (applying Voluntary Offer Agreement) |
| B) Signing, ratifying, and implementing an Additional Protocol | (4) | 0 (not signing); 1 (not ratifying); 3 (in force); add 1 point if widely applied to peaceful nuclear activities |
| 4. Cooperation with the IAEA | 4 | |
| Cooperation with the IAEA | (4) | Add 1 (contributing to the development of verification technologies); add 1~2 (contributing to the universalization of the Additional Protocol); add 1 (other efforts) |
| 5. Implementing Appropriate Export Controls on Nuclear-Related Items and Technologies | 15 | |
| A) Establishment and implementation of the national control systems | (5) | 0 (not establishing); 1 (establishing but insufficient); 2 (establishing a system to a certain degree); 3 (establishing an advanced system, including the Catch-all); add 1~2 (if continuing to implement appropriate export controls); deduct 1~2 (not adequately implementing) |
| B) Requiring the conclusion of an Additional Protocol for nuclear export | (2) | 0 (not requiring or no information); 1 (requiring for some cases); 2 (requiring) |
| C) Implementation of the UNSCRs concerning North Korean and Iranian nuclear issues | (3) | 0 (not implementing or no information); 2 (implementing); 3(actively implementing); deduct 1~3 (depending on the degree of violation) |
| D) Participation in the PSI | (2) | 0 (not participating); 1 (participating); 2 (actively participating) |
| E) Civil nuclear cooperation with non-parties to the NPT | (3) | 0 (exploring active cooperation); 1~2 (contemplating cooperation, subject to implementing additional nuclear disarmament and non-proliferation measures); 3 (showing a cautious attitude or being against it) |
| 6. Transparency in the Peaceful Use of Nuclear Energy | 4 | |
| A) Reporting on the peaceful nuclear activities | (2) | 0 (not reporting or no information); 1 (reporting but insufficiently); 2 (reporting) |
| B) Reporting on plutonium management | (2) | 0 (not reporting or no information); 1 (reporting); 2 (reporting on not only plutonium but also uranium);add 1 (ensuring a high level of transparency in plutonium although not being obliged to report) |
【Nuclear Security]】
| Evaluation criteria | Maximum points |
Scale of measurement |
| 1. The Amount of Fissile Material Usable for Weapons | -16 | |
| The amount of fissile material usable for weapons | (-16) | Firstly, -3 (if possessing fissile material usable for nuclear weapons). Then, deduct as follows: ・ HEU: -5 (>100t); -4 (>20t); -3 (>10t); -2 (>1t); -1 (possessing less than 1t) ・Weapon-grade Pu: -5 (>100t); -4 (>20t); -3 (>10t); -2 (>1t); -1 (possessing less than 1t) ・Reactor-grade Pu: -3 (>10t); -2 (>1t); -1 (possessing less than 1t) |
| 2. Status of Accession to Nuclear Security and Safety-Related Conventions, Participation in Nuclear Security-Related Initiatives, and Application to Domestic Systems | 21 | |
| A) Convention on the Physical Protection of Nuclear Material and the 2005 Amendment to the Convention | (3) | 0 (not signing the Convention); 1 (not ratifying the Convention); 2 (Convention in force, not ratifying the Amendment); 3 (both the Convention and the Amendment in force) |
| B) International Convention for the Suppression of Acts of Nuclear Terrorism | (2) | 0 (not signing); 1 (not ratifying); 2 (in force) |
| C) Convention on Nuclear Safety | (2) | 0 (not signing); 1 (not ratifying); 2 (in force) |
| D) Convention on Early Notification of a Nuclear Accident | (2) | 0 (not signing); 1 (not ratifying); 2 (in force) |
| E) Joint Convention on the Safety of Spent Fuel Management and on the Safety of Radioactive Waste Management | (2) | 0 (not signing); 1 (not ratifying); 2 (in force) |
| F) Convention on Assistance in Case of a Nuclear Accident or Radiological Emergency | (2) | 0 (not signing); 1 (not ratifying); 2 (in force) |
| G) INFCIRC/225/Rev.5 | (4) | 0 (not applying or no information); 2~3 (applying to the national implementation system); 4 (applying and implementing adequately) |
| H) Enactment of laws and establishment of regulations for the national implementation | (4) | 0 (not establishing domestic laws and regulations and the national implementation system); 1~3 (establishing them but insufficient); 4 (establishing appropriately) |
| 3. Efforts to Maintain and Improve the Highest Level of Nuclear Security | 20 | |
| A) Minimization of HEU and separated plutonium stockpile in civilian use | (4) | 0 (no effort or no information); 1 (limited efforts); 3 (active efforts); add 1 (committed to further enhancement) |
| B) Prevention of illicit trafficking | (5) | 0 (not implementing or no information); 2 (limited implementation); 4 (active implementation); add 1 (committed to further enhancement) |
| C) Acceptance of international nuclear security review missions | (2) | 0 (not accepting or no information); 1 (accepting); 2 (actively accepting) |
| D) Technology development―nuclear forensics | (2) | 0 (not implementing or no information); 1 (implementing); 2 (actively implementing) |
| E) Capacity building and support activities | (2) | 0 (not implementing or no information); 1 (implementing); 2 (actively implementing) |
| F) IAEA Nuclear Security Plan and Nuclear Security Fund | (2) | 0 (no effort or information); 1 (participating); 2 (actively participating) |
| G) Participation in international efforts | (3) | 0 (not participating); 1 (participating in a few frameworks); 2 (participating in many or all frameworks); add 1 (if contributing actively) |
As for the evaluation section, a set of objective evaluation criteria is established by which the respective country’s performance is assessed.
The Research Committee of this project recognizes the difficulties, limitations and risk of “scoring” countries’ performances. However, the Committee also considers that an indicative approach is useful to draw attention to nuclear issues, so as to prompt debates over priorities and urgency.
The different numerical values within each category (i.e., nuclear disarmament, nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security) reflect each activity’s importance within that area, as determined through deliberation by the Research Committee of this project. However, the differences in the scoring arrangements within each of the three categories do not necessarily reflect a category’s relative significance in comparison with others, as it has been driven by the differing number of items surveyed. Thus, the value assigned to nuclear disarmament (maximum of 101 points) does not mean that it is more than twice as important as nuclear nonproliferation (maximum of 61 points) or nuclear security (maximum of 41 points).
Regarding “the number of nuclear weapons” (in the Nuclear Disarmament section) and “the amount of fissile material usable for nuclear weapons” (in the Nuclear Security section), the assumption is that the more nuclear weapons or weapons-usable fissile material a country possesses, the greater the task of reducing them and ensuring their security. However, the Research Committee recognizes that “numbers” or “amounts” are not the sole decisive factors. It is definitely true that other factors—such as implications of missile defense, chemical and biological weapons, or conventional force imbalance and a psychological attachment to a minimum overt or covert nuclear weapon capability—would affect the issues and the process of nuclear disarmament, non-proliferation and nuclear security. However, they were not included in our criteria for evaluation because it was difficult to make objective scales of the significance of these factors. In addition, in view of the suggestions and comments made to the Hiroshima Report 2013, the Research Committee modified the criteria of the following items: current status of the roles and significance of nuclear weapons in national security strategies and policies; reliance on extended nuclear deterrence; and nuclear testing.
In the end, there is no way to mathematically compare the different factors contained in the different areas of disarmament, non-proliferation and nuclear security. Therefore, the evaluation points should be taken as indicative of performances in general but by no means as an exact representation or precise assessment of different countries’ performances. Since the Hiroshima Report 2014, such items as “relying on extended nuclear deterrence” and “nuclear testing” have been negatively graded if applicable.
Along with the adoption of the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW), its signature and ratification status was newly added to the evaluation item in the Hiroshima Report 2018. In addition, since the Hiroshima Report 2019, the Research Committee has added an evaluation item addressing whether the respective countries attended the Hiroshima or the Nagasaki Peace Memorial Ceremonies, while attendance at the Hiroshima Peace Memorial Ceremony alone had been evaluated until the Hiroshima Report 2018. (the maximum score in this item remains the same). Since the Hiroshima Report 2020, increase of the number of possessed nuclear weapons in the past five years without any reductions, and activities that are not covered by the existing evaluation items but contrary to nuclear disarmament and non-proliferation are negatively graded, if applicable. Furthermore, since the Hiroshima Report 2021, the Research Committee modified grading range as follows: grading range of negative evaluation on actions against nuclear non-proliferation has been expanded; grading range on the IAEA “Recommendations on the Physical Protection of Nuclear Material and Facilities (INFCIRC/225/Rev.5),” has been expanded and measures against insider threat and cyber threat have been positively evaluated; grading range on enactment of laws and establishment of regulations for national implementation has been expanded. In addition, not only efforts made in 2021 but also previous efforts have been evaluated.
For the NWS, radar charts were produced to illustrate where each country stands with respect to different aspects of nuclear disarmament. For this purpose, the 12 issues used for nuclear disarmament evaluation were grouped into six aspects: (1) the number of nuclear weapons, (2) reduction of nuclear weapons, (3) commitment to achieving a “world without nuclear weapons,” (4) operational policy, (5) the status of signature and ratification of, or attitudes of negotiation to relevant multilateral treaties, and (6) transparency.





