Nuclear Non-Proliferation TreatyNuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty(NPT)
In April 2020, NPT Review Conference will be held in New York. NPT has the important role toward the abolition of nuclear weapons.
1. What is NPT?
NPT stands for the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. During the cold war, the negotiation toward the abolition of nuclear weapons was stagnated. Moreover, the number of countries which sought to acquire nuclear weapons or had potential to produce nuclear weapons increased. Thus, it is believed that the prevention of spreading nuclear weapons leads to abolish nuclear weapons. NPT opened for signature in 1968 and entered in to force in 1970.
NPT has 191 adherents (including North Korea, the Holy See and Palestine). Among the current 193 United nations Member states. India and Pakistan, both of which has nuclear weapons, Israel, which is widely believed to possess them, and South Sudan, which joined the UN in 2011, and does not possess any nuclear weapons are remaining outside the NPT.
2. Nuclear-Weapon States and Non-Nuclear Weapon States
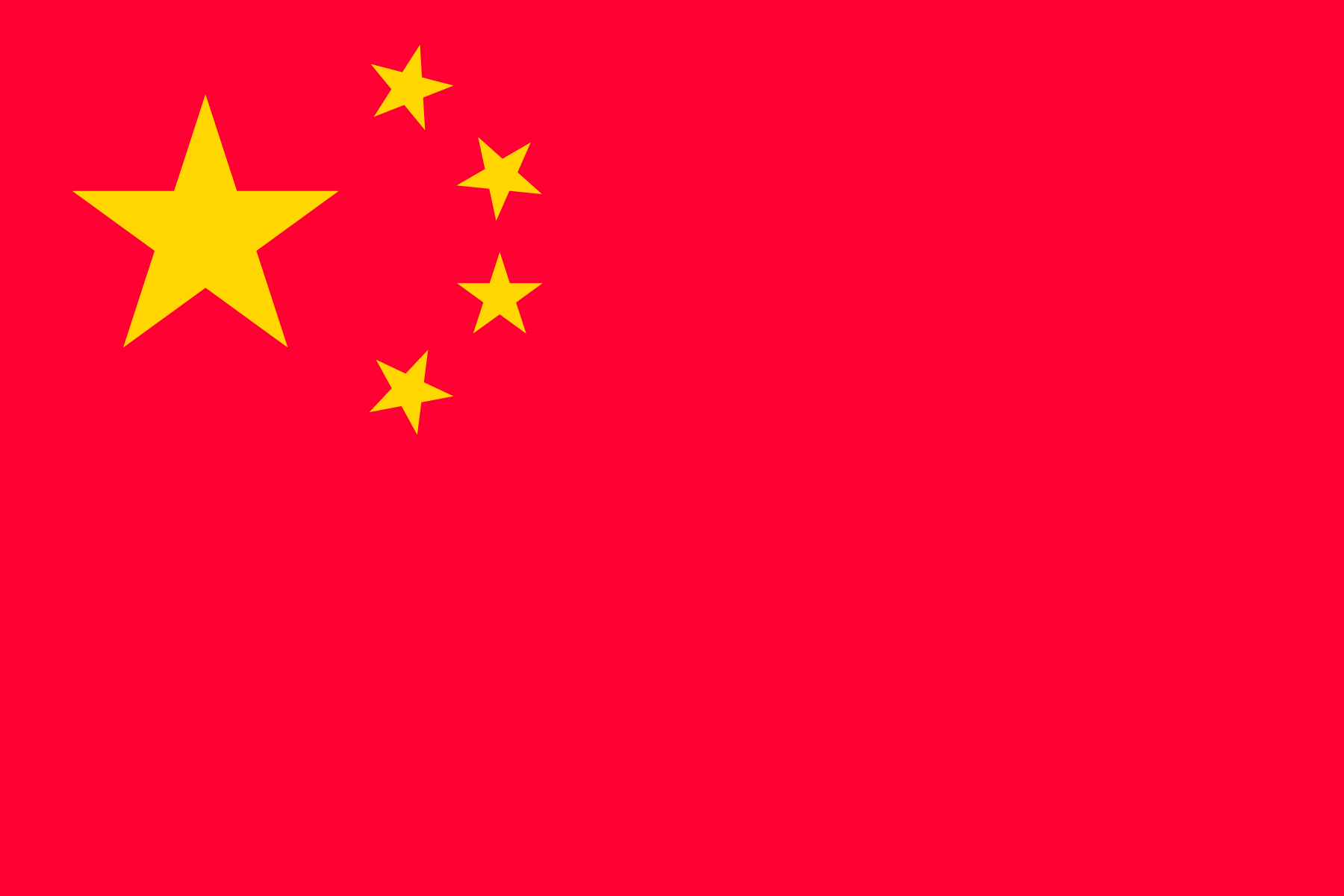
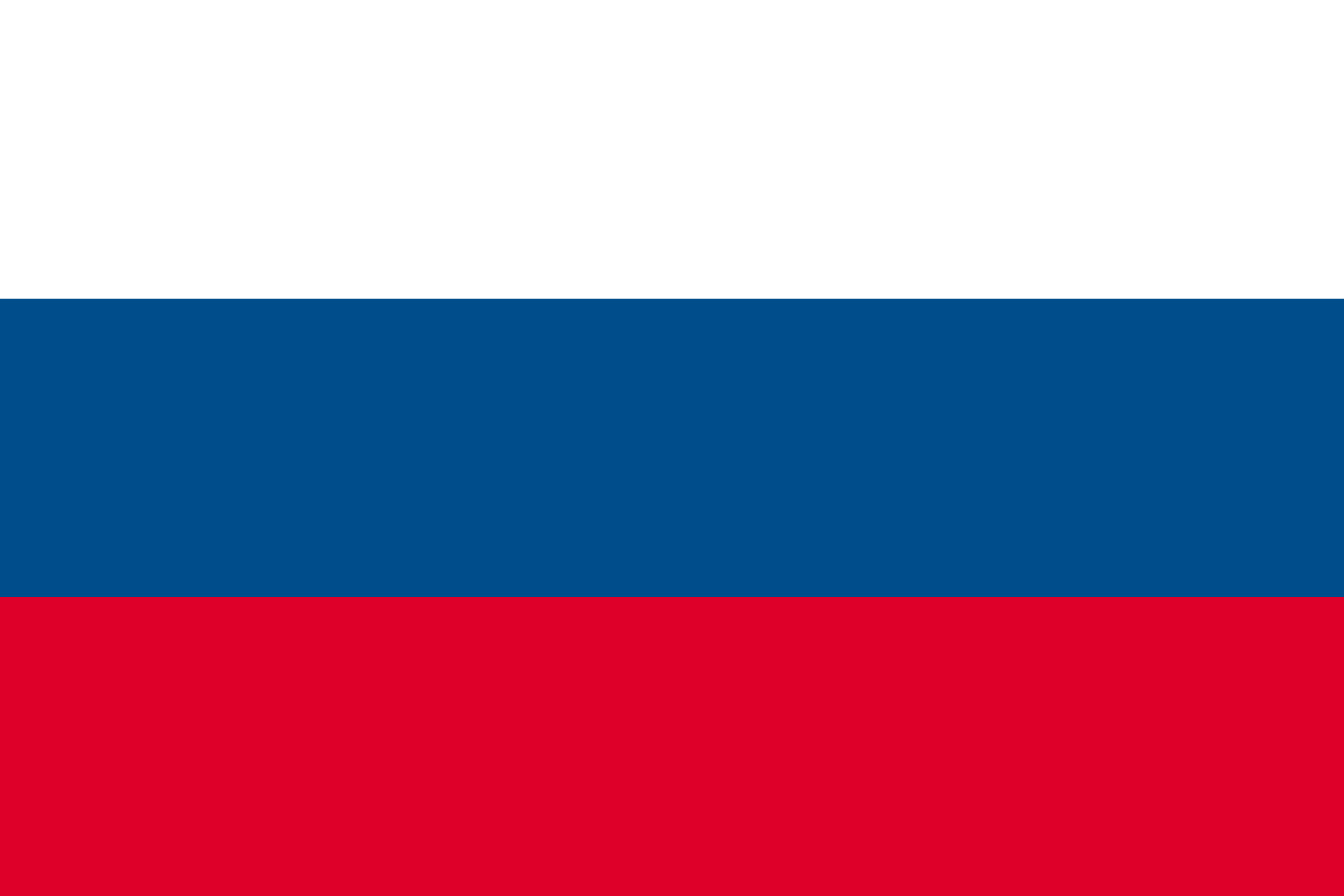
According to Article IV-3 of NPT, “a nuclear-weapon State (NWS) is one which has manufactured and exploded a nuclear weapon or other nuclear explosive device prior to 1 January 1967.”China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States meet this requirement and have acceded to the NPT as NWS as defined by the treaty. Under Article III-1 of the NPT, “each Non-Nuclear Weapon State (NNWS) to the treaty undertakes to accept safeguards as set forth in an agreement to be negotiated and concluded with the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) in accordance with the Statute of the IAEA and the Agency’s safeguards system, for the exclusive purpose of verification of the fulfillment of its obligations assumed under this Treaty with a view to preventing diversion of nuclear energy from peaceful uses to nuclear weapons or other nuclear explosive devices.”
 |
 |
 |
 |
3. Three pillars of NPT
The three pillars of NPT are nuclear non-proliferation, nuclear disarmament and peaceful use of nuclear power. One of the main aims of NPT is nuclear non-proliferation. NPT has a discriminative nature that the obligation to NNWS and NWS is different. Thus, in order to alleviate this nature, state parties including NWS undertake to pursue negotiations in good faith on effective measures relating to cessation of the nuclear arms race at an early date and to nuclear disarmament. In addition, Article IV of NPT acknowledges the “inalienable right” of states parties to research, develop, and use nuclear energy for peaceful purposes.
4. NPT Review Conference
The NPT Review Conference is held every five years to assess the implementation of the treaty. The 2015 NPT Review Conference was not able to reach the agreement Thus, the world focuses on its attention on the initiatives of each state parties toward the 2020 NPT Review Conference.
5. North Korea and Iran
North Korea conducted nuclear tests in 2006, 2009 2013, twice in 2016 and 2017 and possesses nuclear weapons. North Korea declared its suspension from the NPT in 1993 and its withdrawal in 2003. However, there is no agreement among the states parties on North Korea’s official NPT status. Iran also threatened to withdraw from the NPT. Although Article X-1 of the NPT contains some guidance on how a state can legitimately withdraw from the treaty, there remains a lack of clarity over some aspects of this process. Since NPT has an important role toward the abolition of nuclear weapons, we need to pay attention of further discussion between state parties.
6. Initiatives of Hiroshima Prefecture
Hiroshima Prefecture participates in the review conference or preparatory committee for NPT. Through this opportunity, we hold the symposium to disseminate our peace initiatives and message toward the abolition of nuclear weapons.

Information related of this article
Joint Research with International Research Institutes
Tags associated with this article







